



The excesive amounts of Carbon Dioxide in the atmosphere heavily impact marine life. The ocean naturally has a PH level above 7 and many marine species require an environment like this. However, because the ocean absorbs around 30% of our CO2, lots of carbon dioxide enters the ocean and decreases the water's PH levels. This makes the ocean water acidic. This process is called ocean acidification. Coral and many shelled species cannot live in an acidic environment and therefore whither and die.

The rise in global temperature can also increase the spread of certain diseases. For example, mosquitoes are know to carry diseases like malaria, an illness that is common in Africa. However, mosquitoes are commonly found in areas of the world that have warm and humid climates, and cannot survive in areas that have cooler weather. If global warming begins to increase, then malaria and other diseases that are carried by mosquitoes will be more commonly found in places that they never were.

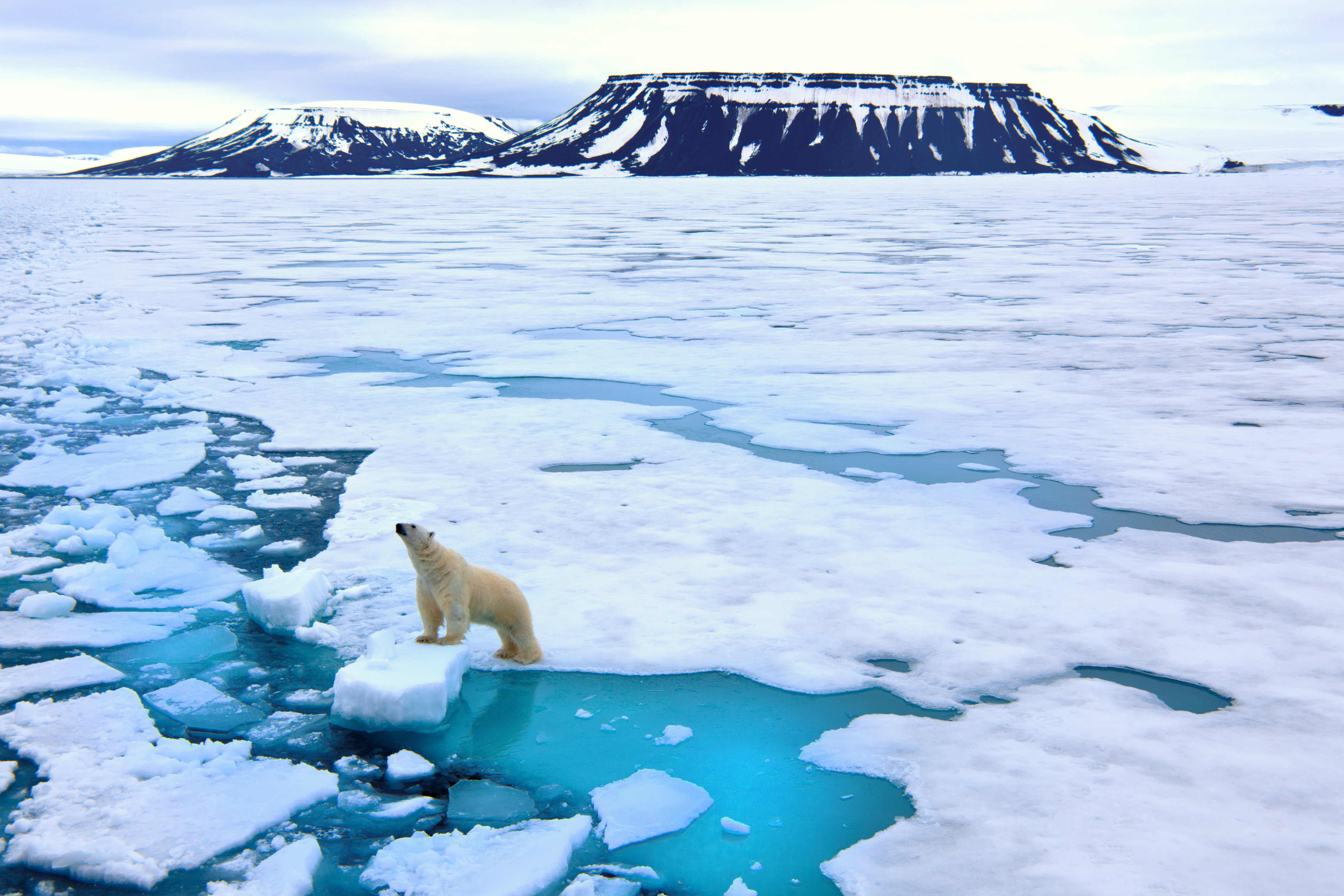
Climate change also puts various species at risk. Every species has a certain type of habitat that they are able to thrive. However, they also can only survive in a certain range of temperatures. As the Earth's average temperature increases, a species habitat may become to warm for them to live in, so they will slowly begin to migrate toward the poles of the northern or southern hemisphere (depending on which side of the equator they're on) in search for a cooler habitat. Unfortunatly, not all species are capable of doing this; a type of species known as specialists can only live in one single type of habitat or use one certain type of resource, meaning that if they migrate anywhere in search of a cooler place to live, they will die anyway due to not having the specific resources that they need. Species that already live close to the poles, such as polar bears, cannot go further up north; along with their habitat melting, it's safe to say that species like polar bears will not be able to live in a world of rising temperatures. This could all lead to species becoming endangered or even extinct, all due to global warming.
Around 25% of our Carbon Dioxide emissions are absorbed by forests and trees. By depleting our forests and excessively cutting down trees, we are further contributing to the amount of CO2 that remains in our atmosphere. Furthermore, Industrial companies we often support like IKEA, directly participate in deforestation. By cutting down trees native populations and animals are depleted of their habitats.

The increase in global temperature mean that glaciers and ice will melt faster than they did in previous years. Melted ice is added to the ocean and increased the amount of water in the ocean, causing a rise in sea levels. This is particularly dangerous because some islands and coastal areas are barely above sea level, and if this continues, then these regions will be submerged underwater. Organisms that live in icy places close to the poles will lose their habitat, and may become endangered or extinct because of this. Glaciers also reflect the Earth's light and heat (this is known as albeito), so with their declining amount, the Earth will only collect more of the sun's heat, resulting in a snowball effect, also known as a positive feedback loop.